
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Drug Regimen
- Efficacy and Safety of Enavogliflozin versus Dapagliflozin as Add-on to Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 24-Week, Double-Blind, Randomized Trial
- Kyung Ah Han, Yong Hyun Kim, Doo Man Kim, Byung Wan Lee, Suk Chon, Tae Seo Sohn, In Kyung Jeong, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Jang Won Son, Jae Jin Nah, Hwa Rang Song, Seong In Cho, Seung-Ah Cho, Kun Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):796-807. Published online February 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0315
- 40,038 View
- 572 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
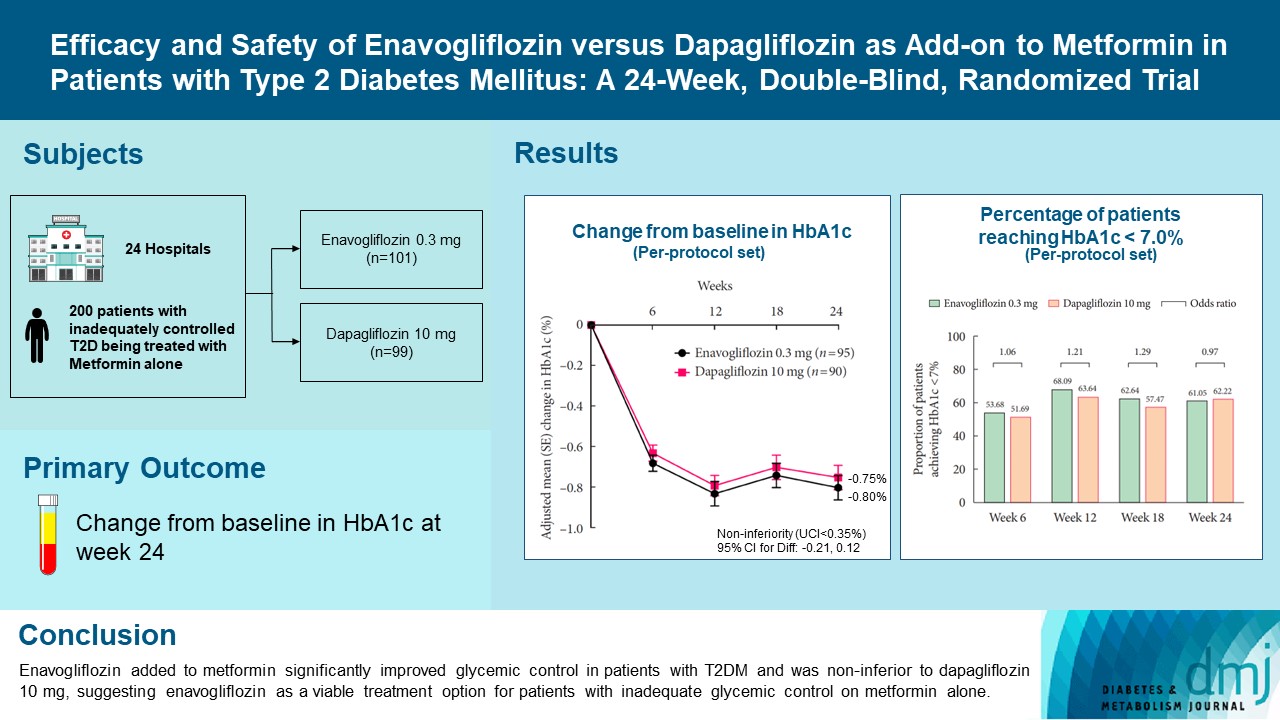
Enavogliflozin is a novel sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor currently under clinical development. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin as an add-on to metformin in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) against dapagliflozin.
Methods
In this multicenter, double-blind, randomized, phase 3 study, 200 patients were randomized to receive enavogliflozin 0.3 mg/day (n=101) or dapagliflozin 10 mg/day (n=99) in addition to ongoing metformin therapy for 24 weeks. The primary objective of the study was to prove the non-inferiority of enavogliflozin to dapagliflozin in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) change at week 24 (non-inferiority margin of 0.35%) (Clinical trial registration number: NCT04634500).
Results
Adjusted mean change of HbA1c at week 24 was –0.80% with enavogliflozin and –0.75% with dapagliflozin (difference, –0.04%; 95% confidence interval, –0.21% to 0.12%). Percentages of patients achieving HbA1c <7.0% were 61% and 62%, respectively. Adjusted mean change of fasting plasma glucose at week 24 was –32.53 and –29.14 mg/dL. An increase in urine glucose-creatinine ratio (60.48 vs. 44.94, P<0.0001) and decrease in homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (–1.85 vs. –1.31, P=0.0041) were significantly greater with enavogliflozin than dapagliflozin at week 24. Beneficial effects of enavogliflozin on body weight (–3.77 kg vs. –3.58 kg) and blood pressure (systolic/diastolic, –5.93/–5.41 mm Hg vs. –6.57/–4.26 mm Hg) were comparable with those of dapagliflozin, and both drugs were safe and well-tolerated.
Conclusion
Enavogliflozin added to metformin significantly improved glycemic control in patients with T2DM and was non-inferior to dapagliflozin 10 mg, suggesting enavogliflozin as a viable treatment option for patients with inadequate glycemic control on metformin alone. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin vs. dapagliflozin as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on renal function: a pooled analysis of two randomized controlled trials
Young Sang Lyu, Sangmo Hong, Si Eun Lee, Bo Young Cho, Cheol-Young Park
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A 52‐week efficacy and safety study of enavogliflozin versus dapagliflozin as an add‐on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: ENHANCE‐M extension study
Tae Seo Sohn, Kyung‐Ah Han, Yonghyun Kim, Byung‐Wan Lee, Suk Chon, In‐Kyung Jeong, Eun‐Gyoung Hong, Jang Won Son, JaeJin Na, Jae Min Cho, Seong In Cho, Wan Huh, Kun‐Ho Yoon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of renal function on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of enavogliflozin, a potent and selective sodium‐glucose cotransporter‐2 inhibitor, in type 2 diabetes
Sae Im Jeong, Mu Seong Ban, Jun‐Gi Hwang, Min‐Kyu Park, Soo Lim, Sejoong Kim, Soon Kil Kwon, Yoonjin Kim, Jae Min Cho, Jae Jin Na, Wan Huh, Jae‐Yong Chung
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of novel sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor enavogliflozin in type-2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, B.G. Harish, Beatrice Anne, Lakshmi Nagendra
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(8): 102816. CrossRef - Characteristics of the Latest Therapeutic Agent for Diabetes
Nuri Yun
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 148. CrossRef - Prospects of using sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors in patients with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD)
Iryna Kostitska, Nadia Protas, Liliia Petrovska
Diabetes Obesity Metabolic Syndrome.2023; (5): 8. CrossRef - Navigating the Future of Diabetes Treatment with New Drugs: Focusing on the Possibilities and Prospects of Enavogliflozin
Sang Youl Rhee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 769. CrossRef
- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin vs. dapagliflozin as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on renal function: a pooled analysis of two randomized controlled trials
- Drug/Regimen
- Comparison of Efficacy of Glimepiride, Alogliptin, and Alogliptin-Pioglitazone as the Initial Periods of Therapy in Patients with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Open-Label, Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Study
- Hae Jin Kim, In Kyung Jeong, Kyu Yeon Hur, Soo-Kyung Kim, Jung Hyun Noh, Sung Wan Chun, Eun Seok Kang, Eun-Jung Rhee, Sung Hee Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):689-700. Published online March 17, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0183
- 5,649 View
- 377 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The choice of an optimal oral hypoglycemic agent in the initial treatment periods for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients remains difficult and deliberate. We compared the efficacy and safety of glimepiride (GLIM), alogliptin (ALO), and alogliptin-pioglitazone (ALO-PIO) in poorly controlled T2DM patients with drug-naïve or metformin failure.
Methods
In this three-arm, multicenter, open-label, randomized, controlled trial, poorly controlled T2DM patients were randomized to receive GLIM (n=35), ALO (n=31), or ALO-PIO (n=33) therapy for 24 weeks. The primary endpoint was change in the mean glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels at week 24 from baseline. Secondary endpoints were changes in HbA1c level at week 12 from baseline, fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels, lipid profiles at weeks 12 and 24, and parameters of glycemic variability, assessed by continuous glucose monitoring for 24 weeks.
Results
At weeks 12 and 24, the ALO-PIO group showed significant reduction in HbA1c levels compared to the ALO group (–0.96%±0.17% vs. –0.37%±0.17% at week 12; –1.13%±0.19% vs. –0.18%±0.2% at week 24). The ALO-PIO therapy caused greater reduction in FPG levels and significant increase in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels at weeks 12 and 24 than the ALO therapy. Compared to low-dose GLIM therapy, ALO-PIO therapy showed greater improvement in glycemic variability. The adverse events were similar among the three arms.
Conclusion
ALO-PIO combination therapy during the early period exerts better glycemic control than ALO monotherapy and excellency in glycemic variability than low-dose sulfonylurea therapy in uncontrolled, drug-naïve or metformin failed T2DM patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comprehensive Review on Weight Loss Associated with Anti-Diabetic Medications
Fatma Haddad, Ghadeer Dokmak, Maryam Bader, Rafik Karaman
Life.2023; 13(4): 1012. CrossRef - Role of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors in Antidiabetic Treatment
Ruili Yin, Yongsong Xu, Xin Wang, Longyan Yang, Dong Zhao
Molecules.2022; 27(10): 3055. CrossRef
- A Comprehensive Review on Weight Loss Associated with Anti-Diabetic Medications
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Efficacy and Safety of Voglibose Plus Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Tae Jung Oh, Jae Myung Yu, Kyung Wan Min, Hyun Shik Son, Moon Kyu Lee, Kun Ho Yoon, Young Duk Song, Joong Yeol Park, In Kyung Jeong, Bong Soo Cha, Yong Seong Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, In Joo Kim, Doo Man Kim, Sung Rae Kim, Kwan Woo Lee, Jeong Hyung Park, In Kyu Lee, Tae Sun Park, Sung Hee Choi, Sung Woo Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(3):276-286. Published online December 7, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0051
- 7,047 View
- 98 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Combination of metformin to reduce the fasting plasma glucose level and an α-glucosidase inhibitor to decrease the postprandial glucose level is expected to generate a complementary effect. We compared the efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose combination of voglibose plus metformin (vogmet) with metformin monotherapy in drug-naïve newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods A total of 187 eligible patients aged 20 to 70 years, with a glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level of 7.0% to 11.0%, were randomized into either vogmet or metformin treatments for 24 weeks. A change in the HbA1c level from baseline was measured at week 24.
Results The reduction in the levels of HbA1c was −1.62%±0.07% in the vogmet group and −1.31%±0.07% in the metformin group (
P =0.003), and significantly more vogmet-treated patients achieved the target HbA1c levels of <6.5% (P =0.002) or <7% (P =0.039). Glycemic variability was also significantly improved with vogmet treatment, estimated by M-values (P =0.004). Gastrointestinal adverse events and hypoglycemia (%) were numerically lower in the vogmet-treated group. Moreover, a significant weight loss was observed with vogmet treatment compared with metformin (−1.63 kg vs. −0.86 kg,P =0.039).Conclusion Vogmet is a safe antihyperglycemic agent that controls blood glucose level effectively, yields weight loss, and is superior to metformin in terms of various key glycemic parameters without increasing the risk of hypoglycemia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Phytochemical analysis and antihyperglycemic activity of Castilleja arvensis
Mónica Aideé Díaz-Román, Juan José Acevedo-Fernández, Gabriela Ávila-Villarreal, Elizabeth Negrete-León, A. Berenice Aguilar-Guadarrama
Fitoterapia.2024; 174: 105839. CrossRef - YAP/TAZ axis was involved in the effects of metformin on breast cancer
Yu Xu, Hongke Cai, Yuanfeng Xiong, Li Tang, Longjiang Li, Li Zhang, Yi Shen, Yongqiang Yang, Ling Lin, Jiayi Huang
Journal of Chemotherapy.2023; 35(7): 627. CrossRef - Diabetes remission: Myth or reality?
Ashok Kumar, ShubhaLaxmi Margekar, Ravi Kumar
Indian Journal of Medical Specialities.2023; 14(1): 3. CrossRef - Analysis of Reports Sent to the Portuguese Pharmacovigilance System and Published Literature Regarding the Safety of Metformin in the Elderly
Beatriz Esteves, Cristina Monteiro, Ana Paula Coelho Duarte
Healthcare.2023; 11(15): 2197. CrossRef - Rapid prediction method of α-Glycosidase inhibitory activity of Coreopsis tinctoria extract from different habitats by near infrared spectroscopy
Xiaogang He, Xiang Han, Jiaping Yu, Yulong Feng, Ganghui Chu
Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy.2022; 268: 120601. CrossRef - Insulin autoimmune syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes: A report of two cases
Y. Shin, T.J. Oh, S.H. Choi, H.C. Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism.2021; 47(1): 101115. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Treatment with Quadruple Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Multi-Center, Retrospective, Observational Study
Jun Sung Moon, Sunghwan Suh, Sang Soo Kim, Heung Yong Jin, Jeong Mi Kim, Min Hee Jang, Kyung Ae Lee, Ju Hyung Lee, Seung Min Chung, Young Sang Lyu, Jin Hwa Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Jung Eun Jang, Tae Nyun Kim, Sung Woo Kim, Eonju Jeon, Nan Hee Cho, Mi-Kyung Ki
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 675. CrossRef - Quantifying Remission Probability in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Sanjay Kalra, Ganapathi Bantwal, Nitin Kapoor, Rakesh Sahay, Saptarshi Bhattacharya, Beatrice Anne, Raju A Gopal, Sunil Kota, Ashok Kumar, Ameya Joshi, Debmalya Sanyal, Mangesh Tiwaskar, Ashok Kumar Das
Clinics and Practice.2021; 11(4): 850. CrossRef - The effect of voglibose on metabolic profiles in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials
Peyman Nowrouzi-Sohrabi, Reza Tabrizi, Shahla Rezaei, Fatemeh Jafari, Kamran Hessami, Mehdi Abedi, Mohammad Jalali, Pedram Keshavarzi, Saeed Shahabi, Ali Asghar Kolahi, Kristin Carson-Chahhoud, Amirhossein Sahebkar, Saeid Safiri
Pharmacological Research.2020; 159: 104988. CrossRef - Role of Intestinal Microbiota in Metabolism of Voglibose In Vitro and In Vivo
Mahesh Raj Nepal, Mi Jeong Kang, Geon Ho Kim, Dong Ho Cha, Ju-Hyun Kim, Tae Cheon Jeong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 908. CrossRef - Response: Efficacy and Safety of Voglibose Plus Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial (Diabetes metab J 2019;43;276-86)
Tae Jung Oh, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 547. CrossRef - Letter: Efficacy and Safety of Voglibose Plus Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43;276-86)
Hannah Seok, Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 545. CrossRef
- Phytochemical analysis and antihyperglycemic activity of Castilleja arvensis
- Epidemiology
- Clinical Characteristics of People with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes between 2015 and 2016: Difference by Age and Body Mass Index
- Kyoung Hwa Ha, Cheol Young Park, In Kyung Jeong, Hyun Jin Kim, Sang-Yong Kim, Won Jun Kim, Ji Sung Yoon, In Joo Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Sungrae Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(2):137-146. Published online February 14, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.42.2.137
- 5,350 View
- 80 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We evaluated the clinical characteristics of insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction in newly diagnosed, drug-naive people with type 2 diabetes by analyzing nationwide cross-sectional data.
Methods We collected the clinical data of 912 participants with newly diagnosed diabetes from 83 primary care clinics and hospitals nationwide from 2015 to 2016. The presence of insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction was defined as a homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) value ≥2.5 and fasting C-peptide levels <1.70 ng/mL, respectively.
Results A total of 75.1% and 22.6% of participants had insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction, respectively. The proportion of participants with insulin resistance but no β-cell dysfunction increased, and the proportion of participants with β-cell dysfunction but no insulin resistance decreased as body mass index (BMI) increased. People diagnosed with diabetes before 40 years of age had significantly higher HOMA-IR and BMI than those diagnosed over 65 years of age (HOMA-IR, 5.0 vs. 3.0; BMI, 28.7 kg/m2 vs. 25.1 kg/m2). However, the β-cell function indices were lower in people diagnosed before 40 years of age than in those diagnosed after 65 years of age (homeostatic model assessment of β-cell function, 39.3 vs. 64.9; insulinogenic index, 10.3 vs. 18.7; disposition index, 0.15 vs. 0.25).
Conclusion We observed that the main pathogenic mechanism of type 2 diabetes is insulin resistance in participants with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. In addition, young adults with diabetes are more likely to have higher insulin resistance with obesity and have higher insulin secretory defect with severe hyperglycemia in the early period of diabetes than older populations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A double‐blind, Randomized controlled trial on glucose‐lowering EFfects and safety of adding 0.25 or 0.5 mg lobeglitazone in type 2 diabetes patients with INadequate control on metformin and dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor therapy: REFIND study
Soree Ryang, Sang Soo Kim, Ji Cheol Bae, Ji Min Han, Su Kyoung Kwon, Young Il Kim, Il Seong Nam‐Goong, Eun Sook Kim, Mi‐kyung Kim, Chang Won Lee, Soyeon Yoo, Gwanpyo Koh, Min Jeong Kwon, Jeong Hyun Park, In Joo Kim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(9): 1800. CrossRef - Apparent Insulin Deficiency in an Adult African Population With New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Davis Kibirige, Isaac Sekitoleko, Priscilla Balungi, William Lumu, Moffat J. Nyirenda
Frontiers in Clinical Diabetes and Healthcare.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Rising Incidence of Diabetes in Young Adults in South Korea: A National Cohort Study
Hyun Ho Choi, Giwoong Choi, Hojun Yoon, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 803. CrossRef - A Real-World Study of Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Lobeglitazone in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Bo-Yeon Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Suk Kyeong Kim, Jung-Hyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Hyeong-Kyu Park, Kee-Ho Song, Jong Chul Won, Jae Myung Yu, Mi Young Lee, Jae Hyuk Lee, Soo Lim, Sung Wan Chun, In-Kyung Jeong, Choon Hee Chung, Seung Jin Han, Hee-Seok Kim, Ju-Y
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 855. CrossRef - The Potential Effect of Rhizoma coptidis on Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking
Liyun Duan, De Jin, Xuedong An, Yuehong Zhang, Shenghui Zhao, Rongrong Zhou, Yingying Duan, Yuqing Zhang, Xinmin Liu, Fengmei Lian, Wen yi Kang
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - PRKAA2variation and the clinical characteristics of patients newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Dita Maria Virginia, Mae Sri Hartati Wahyuningsih, Dwi Aris Agung Nugrahaningsih
Asian Biomedicine.2021; 15(4): 161. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Pioglitazone versus Glimepiride after Metformin and Alogliptin Combination Therapy: A Randomized, Open-Label, Multicenter, Parallel-Controlled Study
Jeong Mi Kim, Sang Soo Kim, Jong Ho Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Tae Nyun Kim, Soon Hee Lee, Chang Won Lee, Ja Young Park, Eun Sook Kim, Kwang Jae Lee, Young Sik Choi, Duk Kyu Kim, In Joo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 67. CrossRef - Favorable Glycemic Control with Once-Daily Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart after Changing from Basal Insulin in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes
Han Na Jang, Ye Seul Yang, Seong Ok Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Bo Kyung Koo, Hye Seung Jung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(4): 382. CrossRef - Insulin Resistance versus β-Cell Failure: Is It Changing in Koreans?
Mi-kyung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(2): 128. CrossRef - Response: Clinical Characteristics of People with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes between 2015 and 2016: Difference by Age and Body Mass Index (Diabetes Metab J2018;42:137-46)
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Sungrae Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(3): 251. CrossRef - Letter: Clinical Characteristics of People with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes between 2015 and 2016: Difference by Age and Body Mass Index (Diabetes Metab J 2018;42:137-46)
Ah Reum Khang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(3): 249. CrossRef
- A double‐blind, Randomized controlled trial on glucose‐lowering EFfects and safety of adding 0.25 or 0.5 mg lobeglitazone in type 2 diabetes patients with INadequate control on metformin and dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor therapy: REFIND study
- The Changes in Early Phase Insulin Secretion in Newly Diagnosed, Drug Naive Korean Prediabetes Subjects
- Sang Youl Rhee, Joo Young Kim, Suk Chon, You Cheol Hwang, In Kyung Jeong, Seungjoon Oh, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Jeong-taek Woo, Sung Woon Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Young Seol Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(3):157-165. Published online June 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.3.157
- 4,533 View
- 28 Download
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background There have been no systematic observations regarding changes in early phase insulin secretion among Korean prediabetes and early stage type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients.
Methods We conducted 75-g oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT) in 873 subjects with suspected abnormal glucose tolerance. All subjects were diagnosed as having normal glucose tolerance (NGT), prediabetes (preDM), or T2DM according to the OGTT results and the insulin secretory and insulin resistance indices of each subject were calculated. Additionally, we analyzed the changes in early phase insulin secretion according to changes in fasting (Glc0), post-prandial (Glc120) glucose and HbA1c (A1c) levels.
Results As compared to subjects with NGT, the insulin secretory indices of the preDM and T2DM subjects progressively declined, and the insulin resistance indices were progressively aggravated. Early phase insulin secretion decreased rapidly according to the increments of Glc0, Glc120 and A1c, and these changes were most prominent in the NGT stage. Compared to the control group, the early phase insulin secretion levels of the preDM or T2DM subjects were less than 50% when Glc0 was over 100 mg/dL, Glc120 was over 145 mg/dL, and A1c was over 5.8%.
Conclusion This study suggests that progressive beta cell dysfunction in Koreans may be initiated and rapidly aggravated during the period generally designated as 'normal.'
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hospital-Based Korean Diabetes Prevention Study: A Prospective, Multi-Center, Randomized, Open-Label Controlled Study
Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Jeong-Taek Woo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(1): 49. CrossRef - Differential role of insulin resistance and β-cell function in the development of prediabetes and diabetes in middle-aged and elderly Chinese population
Xueli Cai, Lili Xia, Yuesong Pan, Dian He, Huiping Zhu, Tiemin Wei, Yan He
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Primary Aldosteronism and Different Therapeutic Modalities on Glucose Metabolism
Mi Kyung Kwak, Jee Yang Lee, Beom-Jun Kim, Seung Hun Lee, Jung-Min Koh
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(12): 2194. CrossRef - Insulin resistance increases the risk of incident type 2 diabetes mellitus in patients with non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease
Yuya Seko, Yoshio Sumida, Saiyu Tanaka, Kojiroh Mori, Hiroyoshi Taketani, Hiroshi Ishiba, Tasuku Hara, Akira Okajima, Atsushi Umemura, Taichiro Nishikawa, Kanji Yamaguchi, Michihisa Moriguchi, Kazuyuki Kanemasa, Kohichiroh Yasui, Shunsuke Imai, Keiji Shim
Hepatology Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Longitudinal Changes in Insulin Resistance, Beta-Cell Function and Glucose Regulation Status in Prediabetes
Chul-Hee Kim, Hong-Kyu Kim, Eun-Hee Kim, Sung-Jin Bae, Jaewon Choe, Joong-Yeol Park
The American Journal of the Medical Sciences.2018; 355(1): 54. CrossRef - Prenatal Dexamethasone Exposure Programs the Development of the Pancreas and the Secretion of Insulin in Rats
Yu-Chieh Chen, Ying-Hua Huang, Jiunn-Ming Sheen, You-Lin Tain, Hong-Ren Yu, Chih-Cheng Chen, Miao-Meng Tiao, Ho-Chang Kuo, Li-Tung Huang
Pediatrics & Neonatology.2017; 58(2): 135. CrossRef - Insulin Secretory Capacity and Insulin Resistance in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Jong-Dai Kim, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(3): 354. CrossRef - The effect of glargine versus glimepiride on pancreatic β-cell function in patients with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled on metformin monotherapy: open-label, randomized, controlled study
Jun Sung Moon, Kyoung Soo Ha, Ji Sung Yoon, Hyoung Woo Lee, Hyun Chul Lee, Kyu Chang Won
Acta Diabetologica.2014; 51(2): 277. CrossRef - Association of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Glucose Metabolism in Subjects With or Without Obesity
Nan Hee Kim, Nam H. Cho, Chang-Ho Yun, Seung Ku Lee, Dae Wui Yoon, Hyun Joo Cho, Jae Hee Ahn, Ji A. Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Dong Seop Choi, Chol Shin
Diabetes Care.2013; 36(12): 3909. CrossRef - Relative contributions of insulin resistance and β‐cell dysfunction to the development of Type 2 diabetes in Koreans
C.‐H. Kim, H.‐K. Kim, E. H. Kim, S. J. Bae, J.‐Y. Park
Diabetic Medicine.2013; 30(9): 1075. CrossRef - Associations among Body Mass Index, Insulin Resistance, and Pancreatic β-Cell Function in Korean Patients with New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Jin Ook Chung, Dong Hyeok Cho, Dong Jin Chung, Min Young Chung
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2012; 27(1): 66. CrossRef - High normal HbA1c levels were associated with impaired insulin secretion without escalating insulin resistance in Japanese individuals: the Toranomon Hospital Health Management Center Study 8 (TOPICS 8)
Y. Heianza, Y. Arase, K. Fujihara, H. Tsuji, K. Saito, S. D. Hsieh, S. Kodama, H. Shimano, N. Yamada, S. Hara, H. Sone
Diabetic Medicine.2012; 29(10): 1285. CrossRef - The Prediabetic Period: Review of Clinical Aspects
Sang Youl Rhee, Jeong-Taek Woo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(2): 107. CrossRef - Predictive characteristics of patients achieving glycaemic control with insulin after sulfonylurea failure
Y.-H. Lee, B.-W. Lee, S. W. Chun, B. S. Cha, H. C. Lee
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2011; 65(10): 1076. CrossRef - Early Insulin Secretory Dysfunction in Korean Prediabetic Subjects: Should We Change the Criteria for "Prediabetes?"
Chul-Hee Kim
Korean Diabetes Journal.2010; 34(3): 154. CrossRef
- Hospital-Based Korean Diabetes Prevention Study: A Prospective, Multi-Center, Randomized, Open-Label Controlled Study
- Effects of Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) on Pancreatic Islets in Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
- Ji Won Kim, Dong Sik Ham, Heon Seok Park, Yu Bai Ahn, Ki Ho Song, Kun Ho Yoon, Ki Dong Yoo, Myung Jun Kim, In Kyung Jeong, Seung Hyun Ko
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(3):185-197. Published online June 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.3.185
- 2,289 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is associated with the development of diabetic complications. However, it is unknown whether systemic VEGF treatment has any effects on the pancreatic islets in an animal model of type 2 diabetes mellitus. METHODS: Anti-VEGF peptide (synthetic ATWLPPR, VEGF receptor type 2 antagonist) was injected into db/db mice for 12 weeks. We analyzed pancreatic islet morphology and quantified beta-cell mass. Endothelial cell proliferation and the severity of islet fibrosis were also measured. VEGF expression in isolated islets was determined using Western blot analysis. RESULTS: When anti-VEGF was administered, db/db mice exhibited more severe hyperglycemia and associated delayed weight gain than non-treated db/db mice. Pancreas weight and pancreatic beta-cell mass were also significantly decreased in the anti-VEGF-treated group. VEGF and VEGF receptor proteins (types 1 and 2) were expressed in the pancreatic islets, and their expression was significantly increased in the db/db group compared with the db/dm group. However, the elevated VEGF expression was significantly reduced by anti-VEGF treatment compared with the db/db group. The anti-VEGF-treated group had more prominent islet fibrosis and islet destruction than db/db mice. Intra-islet endothelial cell proliferation was also remarkably reduced by the anti-VEGF peptide. CONCLUSION: Inhibition of VEGF action by the VEGF receptor 2 antagonist not only suppressed the proliferation of intra-islet endothelial cells but also accelerated pancreatic islet destruction and aggravated hyperglycemia in a type 2 diabetes mouse model. Therefore, the potential effects of anti-VEGF treatment on pancreatic beta cell damage should be considered.
- A Nationwide Survey about the Current Status of Glycemic Control and Complications in Diabetic Patients in 2006: The Committee of the Korean Diabetes Association on the Epidemiology of Diabetes Mellitus.
- Soo Lim, Dae Jung Kim, In Kyung Jeong, Hyun Shik Son, Choon Hee Chung, Gwanpyo Koh, Dae Ho Lee, Kyu Chang Won, Jeong Hyun Park, Tae Sun Park, Jihyun Ahn, Jaetaek Kim, Keun Gyu Park, Seung Hyun Ko, Yu Bae Ahn, Inkyu Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(1):48-57. Published online February 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.1.48
- 2,770 View
- 55 Download
- 43 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The Committee of the Korean Diabetes Association on the Epidemiology of Diabetes Mellitus performed a nationwide survey about the current status of glycemic control and diabetic complications in 2006. METHODS: The current study included 5,652 diabetic patients recruited from the rosters of endocrinology clinics of 13 tertiary hospitals in Korea. Age, gender, height, weight, waist circumference and blood pressure were investigated by standard method. Fasting and postprandial 2 hour glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), lipid profiles, fasting insulin and c-peptide levels were measured. Microvascular (microalbuminuria, retinopathy and neuropathy) and macrovascular (coronary artery disease [CAD], cerebrovascular disease [CVD] and peripheral artery disease [PAD]) complications were reviewed in their medical records. RESULTS: Mean age of total subjects was 58.7 (+/- 11.6) years and duration of diabetes was 8.8 (0~50) years. Mean fasting and postprandial 2 hour glucose levels were 145.9 +/- 55.0 and 208.0 +/- 84.4 mg/dL, respectively. Their mean HbA1c was 7.9 +/- 1.9%: the percentage of patients within target goal of glycemic control (< 7% of HbA1c) was 36.7%. In this study, 30.3%, 38.3% and 44.6% of patients was found to have microalbuminuria, retinopathy and nephropathy, respectively. Prevalence of CAD, CVD and PAD was 8.7%, 6.7% and 3.0%, respectively. Diabetic complications were closely related with age, duration of diabetes and glycemic control, and this relationship was stronger in microvascular complications than macrovascular ones. CONCLUSION: Only about one third of patients with diabetes was found to reach target glycemic control in tertiary hospitals of Korea. More tight control is needed to reduce deleterious complications of diabetes in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk of Diabetic Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with Dementia: A Population-Based Study Using National Health Insurance Claims Data
Eun Sik Jeong, Ah-Young Kim, Hye-Young Kang
Drug Targets and Therapeutics.2023; 2(1): 49. CrossRef - Prevalence of thyroid disorders in type 2 diabetic patients – A 1-year cross-sectional study
RikitaRamesh Mudhol, ShivakumarVeeranna Turamari, RekhaRamesh Mudhol, B Srinivas
BLDE University Journal of Health Sciences.2022; 7(1): 56. CrossRef - Associations of fasting glucose and glycated hemoglobin with vitamin D levels according to diabetes mellitus status in Korean adults
Yerin Hwang, Jiyoung Jang, Myung-Hee Shin
Epidemiology and Health.2022; 44: e2022025. CrossRef - Atherectomy in Peripheral Artery Disease: Current and Future
Yohan Kwon, Jinoo Kim, Je-Hwan Won, Seong Ho Kim, Jeong-Eun Kim, Sung-Joon Park
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2021; 82(3): 551. CrossRef - Diabetic Retinopathy and Related Clinical Practice for People with Diabetes in Korea: A 10-Year Trend Analysis
Yoo-Ri Chung, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Kihwang Lee, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 928. CrossRef - Current status of treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Ningbo, China
Tianmeng Yang, Rongjiong Zheng, Qingmei Chen, Yushan Mao
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Recently Uncontrolled Glycemia in Diabetic Patients Is Associated with the Severity of Intracranial Atherosclerosis
Nari Choi, Jeong-Yoon Lee, Jun-Sang Sunwoo, Hakjae Roh, Moo-Young Ahn, Sung-Tae Park, Kyung Bok Lee
Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases.2017; 26(11): 2615. CrossRef - The effect of educational program based on the precede-proceed model on improving self-care behaviors in a semi-urban population with type 2 diabetes referred to health centers of Bavi, Iran
Neda Barasheh, Ghodratollah Shakerinejad, Sedigheh Nouhjah, Mohammad Hossein Haghighizadeh
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2017; 11: S759. CrossRef - Increased prevalence of albuminuria in individuals with higher range of impaired fasting glucose: the 2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jong Chul Won, Jae Won Hong, Jung Min Kim, Tae Nyun Kim, Jung Hyun Noh, Kyung Soo Ko, Byoung Doo Rhee, Dong-Jun Kim
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2015; 29(1): 50. CrossRef - Assessment of glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with metformin–sulfonylurea combination: Results of a multicenter, cross‐sectional, observational study in Korea
Sin Gon Kim, Jong Ryeal Hahm, Duk Kyu Kim, Sung Rae Cho, Dong Seop Choi
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2015; 6(3): 317. CrossRef - Current Status of Management in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at General Hospitals in South Korea
Jin-Hee Jung, Jung-Hwa Lee, Jin-Won Noh, Jeong-Eun Park, Hee-Sook Kim, Joo-Wha Yoo, Bok-Rye Song, Jeong-rim Lee, Myeong-Hee Hong, Hyang-Mi Jang, Young Na, Hyun-Joo Lee, Jeong-Mi Lee, Yang-Gyo Kang, Sun-Young Kim, Kang-Hee Sim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(4): 307. CrossRef - Kidney injury molecule-1 (Kim-1): an early biomarker for nephropathy in type II diabetic patients
Nahla E. El-Ashmawy, Enas A. El-Zamarany, Naglaa F. Khedr, Abeer I. Abd El-Fattah, Shereen A. Eltoukhy
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2015; 35(S3): 431. CrossRef - The Effect of the Experience of Diabetes Education on Knowledge, Self-Care Behavior and Glycosylated Hemoglobin in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Seung Hei Moon, Young Whee Lee, Ok-Kyung Ham, Soo-Hyun Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(1): 81. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of Diabetic Patients Transferred to Korean Referral Hospitals
Min Young Oh, Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim, In Kyu Lee, Hong Sun Baek, Hyoung Woo Lee, Min Young Chung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(5): 388. CrossRef - Current Status of Prescription in Type 2 Diabetic Patients from General Hospitals in Busan
Ji Hye Suk, Chang Won Lee, Sung Pyo Son, Min Cheol Kim, Jun Hyeob Ahn, Kwang Jae Lee, Ja Young Park, Sun Hye Shin, Min Jeong Kwon, Sang Soo Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Soon Hee Lee, Jeong Hyun Park, In Joo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(3): 230. CrossRef - The Influence of Admission Hypoglycemia on Clinical Outcomes in Acute Myocardial Infarction Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Eun Jung Kim, Myung Ho Jeong, In Seok Jeong, Sang Gi Oh, Sang Hyung Kim, Young keun Ahn, Ju Han Kim, Young Jo Kim, Shung Chull Chae, Taek Jong Hong, In Whan Seong, Jei Keon Chae, Chong Jin Kim, Myeong Chan Cho, Ki Bae Seung, Hyo Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Medicine.2014; 87(5): 565. CrossRef - Duration of diabetes and effectiveness of insulin in the management of insulin-naïve Korean patients uncontrolled on oral antidiabetic drugs: a sub-analysis of the MOdaliTy of Insulin treatment eValuation (MOTIV) registry results
Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim, Yong Ki Kim, Kun Ho Yoon, Ho Young Son, Sung Woo Park, Yeon Ah Sung, Hong Sun Baek, Kyoung Soo Ha
Acta Diabetologica.2014; 51(4): 655. CrossRef - Is the Indicator Magnifying Window for Insulin Pens Helpful for Elderly Diabetic Patients?
Ju Hee Lee, Eun Shil Hong, Jung Hun Ohn, Young Min Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(2): 149. CrossRef - Prevalence of and Factors Associated with Albuminuria in the Korean Adult Population: The 2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jong Chul Won, Yun Jeong Lee, Jung Min Kim, Sang Youb Han, Jung Hyun Noh, Kyung Soo Ko, Byoung Doo Rhee, Dong-Jun Kim, Harald Mischak
PLoS ONE.2013; 8(12): e83273. CrossRef - The Epidemiology of Diabetic Nephropathy
Jin Hwa Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2013; 14(1): 11. CrossRef - The Relationship between Neuropathic Pain and Glycemic Control, Self Management in Type II Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Yeong-Mi Seo, Won-Hee Choi
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(4): 1774. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Biphasic Insulin Aspart 30/70 in Type 2 Diabetes Suboptimally Controlled on Oral Antidiabetic Therapy in Korea: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Single-Arm Study
Kee-Ho Song, Jung Min Kim, Jung-Hyun Noh, Yongsoo Park, Hyun-Shik Son, Kyong Wan Min, Kyung Soo Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(2): 117. CrossRef - Comorbidity Study on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Using Data Mining
Hye Soon Kim, A Mi Shin, Mi Kyung Kim, Yoon Nyun Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2012; 27(2): 197. CrossRef - Low ankle-brachial index is an independent predictor of poor functional outcome in acute cerebral infarction
Jinkwon Kim, Dong Hyun Lee, Myoung-Jin Cha, Tae-Jin Song, Ji Hye Park, Hye Sun Lee, Chung Mo Nam, Hyo Suk Nam, Young Dae Kim, Ji Hoe Heo
Atherosclerosis.2012; 224(1): 113. CrossRef - Glucose, Blood Pressure, and Lipid Control in Korean Adults with Diagnosed Diabetes
Sun-Joo Boo
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(4): 406. CrossRef - Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
Seung-Hyun Ko, Bong-Yun Cha
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2012; 36(1): 6. CrossRef - The Association of Self-Reported Coronary Heart Disease with Diabetes Duration in Korea
Hye Mi Kang, Yun Jeong Lee, Dong-Jun Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2012; 36(5): 350. CrossRef - Response: The Prevalence of Peripheral Arterial Disease in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Attending a University Hospital (Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:543-50)
Ji Hee Yu, Ki-Up Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2012; 36(1): 77. CrossRef - Reduction in glycated albumin can predict change in HbA1c: comparison of oral hypoglycaemic agent and insulin treatments
H. K. Won, K. J. Kim, B.‐W. Lee, E. S. Kang, B. S. Cha, H. C. Lee
Diabetic Medicine.2012; 29(1): 74. CrossRef - Management of Blood Pressure in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Survey in Korean
Mi Hae Seo, Woo Je Lee, Cheol Young Park, Sung Rae Kim, Joong Yeol Park, Kun-Ho Yoon, Moon Kyu Lee, Sung Woo Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(4): 348. CrossRef - Accuracy Evaluation of the Alternative Site Blood Glucose Test Using Error Grid
Kyung-Soon Park, Eun-Jong Cha
Journal of Biomedical Engineering Research.2011; 32(1): 25. CrossRef - Glycated albumin is a useful glycation index for monitoring fluctuating and poorly controlled type 2 diabetic patients
Eun Young Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Daham Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Kwang Joon Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Jig Lee, Hyun Chul Lee
Acta Diabetologica.2011; 48(2): 167. CrossRef - Group Classification on Management Behavior of Diabetic Mellitus
Sung-Hong Kang, Soon-Ho Choi
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2011; 12(2): 765. CrossRef - Predictive Clinical Parameters for the Therapeutic Efficacy of Sitagliptin in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Soon Ae Kim, Woo Ho Shim, Eun Hae Lee, Young Mi Lee, Sun Hee Beom, Eun Sook Kim, Jeong Seon Yoo, Ji Sun Nam, Min Ho Cho, Jong Suk Park, Chul Woo Ahn, Kyung Rae Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(2): 159. CrossRef - Epidemiology of Micro- and Macrovascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes in Korea
Jung Hee Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(6): 571. CrossRef - Increasing Trend in the Number of Severe Hypoglycemia Patients in Korea
Jin Taek Kim, Tae Jung Oh, Ye An Lee, Jun Ho Bae, Hyo Jeong Kim, Hye Seung Jung, Young Min Cho, Kyong Soo Park, Soo Lim, Hak Chul Jang, Hong Kyu Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(2): 166. CrossRef - Prevalence and Associated Factors of Diabetic Retinopathy in Rural Korea: The Chungju Metabolic Disease Cohort Study
Ji-Hyun Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Yong-Moon Park, Jin-Hee Lee, Man-Soo Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Won Chul Lee, Bong-Yun Cha, Ho-Young Son
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2011; 26(8): 1068. CrossRef - The Prevalence of Peripheral Arterial Disease in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Attending a University Hospital
Ji Hee Yu, Jenie Yoonoo Hwang, Mi-Seon Shin, Chang Hee Jung, Eun Hee Kim, Sang Ah Lee, Eun Hee Koh, Woo Je Lee, Min-Seon Kim, Joong-Yeol Park, Ki-Up Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(5): 543. CrossRef - Prevalence, Awareness, and Control of Hypertension among Diabetic Koreans
Hyun Hee Chung, Kyu Chang Won
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(4): 337. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Physical Activity Behavior among Iranian Women with Type 2 Diabetes Using the Extended Theory of Reasoned Action
Alireza Didarloo, Davoud Shojaeizadeh, Hassan Eftekhar Ardebili, Shamsaddin Niknami, Ebrahim Hajizadeh, Mohammad Alizadeh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(5): 513. CrossRef - Factors that Affect Medication Adherence in Elderly Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung-Ae Park, Jung-Guk Kim, Bo-Wan Kim, Sin Kam, Keon-Yeop Kim, Sung-Woo Ha, Sung-Taek Hyun
Korean Diabetes Journal.2010; 34(1): 55. CrossRef - The Effects of Tailored Diabetes Education on Blood Glucose Control and Self-Care
Kyung Sun Hyun, Kwang Mi Kim, Sook Hee Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(5): 720. CrossRef - Epidemiologic Characteristics of Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: Current Status of Diabetic Patients Using Korean Health Insurance Database
Ie Byung Park, Sei Hyun Baik
Korean Diabetes Journal.2009; 33(5): 357. CrossRef
- Risk of Diabetic Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with Dementia: A Population-Based Study Using National Health Insurance Claims Data
- Prevalence of the Metabolic Syndrome in Type 2 Diabetic Patients.
- Tae Ho Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Soo Lim, In Kyung Jeong, Hyun Shik Son, Choon Hee Chung, Gwanpyo Koh, Dae Ho Lee, Kyu Chang Won, Jeong Hyun Park, Tae Sun Park, Jihyun Ahn, Jaetaek Kim, Keun Gyu Park, Seung Hyun Ko, Yu Bae Ahn, Inkyu Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(1):40-47. Published online February 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.1.40
- 2,379 View
- 27 Download
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The aim of this study was to analyze the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Korean type 2 diabetic patients. METHODS: A total of 4,240 diabetic patients (male 2,033, female 2,207; mean age 58.7 +/- 11.3 years; DM duration 8.9 +/- 7.6 years) were selected from the data of endocrine clinics of 13 university hospitals in 2006. Metabolic syndrome was defined using the criteria of the American Heart Association/National Heart Lung and Blood Institute and the criteria of waist circumference from the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. RESULTS: The prevalence of metabolic syndrome was 77.9% (76.7% of males, 78.9% of females). The average number of the components of metabolic syndrome was 2.4 +/- 1.1. Abdominal obesity was seen in 56.8% of the patients, hypertriglyceridemia in 42.0%, low HDL cholesterol in 65.1%, and high blood pressure in 74.9%. Abdominal obesity and high blood pressure were much more prevalent among females than males, and low HDL cholesterol was much more prevalent among males than females. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome was not different according to the duration of diabetes. Metabolic syndrome was strongly related with obesity (odds ratio, 6.3) and increased age (odds ratio in the over 70 group, 3.4). CONCLUSION: The prevalence of metabolic syndrome was 77.9% in Korean type 2 diabetic patients. Its prevalence was greater in obese patients and in those over 40 years of age. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Novel Clinical Predictor of Metabolic Syndrome: Vascular Risk Age
Abdulrahman Naser, Didar Elif Akgün, Rengin Çetin Güvenç, Samet Sayılan, Özgen Şafak
Bagcilar Medical Bulletin.2023; 9(1): 1. CrossRef - Risk of Carotid Atherosclerosis in Subjects with Prediabetes Overlapping Metabolic Syndrome
Seol A Jang, Kyoung Min Kim, Seok Won Park, Chul Sik Kim
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2022; 20(10): 599. CrossRef - Metabolic Age, an Index Based on Basal Metabolic Rate, Can Predict Individuals That are High Risk of Developing Metabolic Syndrome
Sarahi Vásquez-Alvarez, Sergio K. Bustamante-Villagomez, Gabriela Vazquez-Marroquin, Leonardo M. Porchia, Ricardo Pérez-Fuentes, Enrique Torres-Rasgado, Oscar Herrera-Fomperosa, Ivette Montes-Arana, M. Elba Gonzalez-Mejia
High Blood Pressure & Cardiovascular Prevention.2021; 28(3): 263. CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome among type 2 diabetic patients in Sub-Saharan African countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Wondimeneh Shibabaw Shiferaw, Tadesse Yirga Akalu, Mihretie Gedefaw, Denis Anthony, Ayelign Mengesha Kassie, Worku Misganaw Kebede, Henok Mulugeta, Getenet Dessie, Yared Asmare Aynalem
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2020; 14(5): 1403. CrossRef - Optimal Waist Circumference Cutoff Value Based on Insulin Resistance and Visceral Obesity in Koreans with Type 2 Diabetes
Jung Soo Lim, Young Ju Choi, Soo-Kyung Kim, Byoung Wook Huh, Eun Jig Lee, Kap Bum Huh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(3): 253. CrossRef - The Relations between Diabetic Dietary Compliance, Dietary Intake, and Physical Activity and the Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome (MS) in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Dong Eun Kim, Seung Hee Hong, Ji-Myung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(5): 351. CrossRef - The Comparison between Periodontal Health Status and the Findings of Hypertension and Diabetes Disease of some Workers
In-Young Ku, Seon-Jeong Moon, Kyung-Hwan Ka, Myeong-Seon Lee
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2013; 7(2): 81. CrossRef - The Relationship between Factors of Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adult Males and the Parents' Family History of Diabetes
Hyung-Su Park, Jin-Gyu Jeong, Jin-Ho Yu
The Journal of the Korea institute of electronic communication sciences.2013; 8(5): 779. CrossRef - Associations of serum fetuin-A levels with insulin resistance and vascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes
Chan-Hee Jung, Bo-Yeon Kim, Chul-Hee Kim, Sung-Koo Kang, Sang-Hee Jung, Ji-Oh Mok
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2013; 10(5): 459. CrossRef - Cardio-Metabolic Features of Type 2 Diabetes Subjects Discordant in the Diagnosis of Metabolic Syndrome
Sa Rah Lee, Ying Han, Ja Won Kim, Ja Young Park, Ji Min Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Mi-Kyoung Park, Hye-Jeong Lee, Duk Kyu Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2012; 36(5): 357. CrossRef - Comorbidity Study on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Using Data Mining
Hye Soon Kim, A Mi Shin, Mi Kyung Kim, Yoon Nyun Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2012; 27(2): 197. CrossRef - Therapeutic Target Achievement in Type 2 Diabetic Patients after Hyperglycemia, Hypertension, Dyslipidemia Management
Ah Young Kang, Su Kyung Park, So Young Park, Hye Jeong Lee, Ying Han, Sa Ra Lee, Sung Hwan Suh, Duk Kyu Kim, Mi Kyoung Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(3): 264. CrossRef - The Correlations between Extremity Circumferences with Total and Regional Amounts of Skeletal Muscle and Muscle Strength in Obese Women with Type 2 Diabetes
Hwi Ryun Kwon, Kyung Ah Han, Hee Jung Ahn, Jae Hyuk Lee, Gang Seo Park, Kyung Wan Min
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(4): 374. CrossRef
- A Novel Clinical Predictor of Metabolic Syndrome: Vascular Risk Age
- Clinical Characteristics and Analysis of Risk Factor for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Diabetic Patient.
- Kwang Hyuk Park, Seong Bo Yoon, Min Ho Jo, Eon Kyung Hong, Seong Jin Lee, In Kyung Jeong, Chul Young Park, Ki Won Oh, Hyun Kyu Kim, Jac Myoung Yu, Doo Man Kim, Sung Hee Lim, Moon Ki Choi, Hyung Jun Yoo, Sung Woo Park, Heung Young Oh, Jin Bae Kim, Il Hyun Baek, Myung Seok Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2005;29(4):358-366. Published online July 1, 2005
- 1,357 View
- 27 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
A high prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease(GERD) has been reported in diabetic patient. However, the exact mechanisms of GERD in diabetic patient have not been described. In several studies, diabetic neuropathy and dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system have been suggested as risk factors of GERD. However, there have been no studies on the exact prevalence or risk factors of GERD in Korean diabetic patients. Therefore, the prevalence of GERD in Korean diabetics patients was examined, and the risk factors for GERD, the differences in symptoms between GERD and non-GERD patients, and the degree of symptom relief after treatment were also analyzed. METHODS: A total of 310 diabetic patients, who underwent an upper gastroendoscopy due to diverse gastrointestinal symptoms, between April 2001 and November 2003, were enrolled. The diagnostic criteria or GERD included the upper gastroendoscopic view, which was analyzed using the scale of 'The Los Angeles Classification of Esophagus' from grades A to D. The prevalence and symptoms of GERD patients and the variable risk factors, such as blood glucose level, smoking and diabetic neuropathy, were examined. RESULTS: 1) There was an 18.4% prevalence of GERD in diabetic patients. 2) The clinical characteristics, including sex, age and serum lipid level, of the GERD group were not significantly different to those of the control group. However, the duration of smoking, the fasting and postprandial 2-hour serum glucose levels, and the diabetic neuropathy significantly affected GERD, 3) The main symptoms of the GERD group were dyspepsia(47.4%) and heart burn(26.3%). 4) The degree of subjective symptom relief in the GERD group after treatment with the proton pump inhibitor, pantoprazole(40mg), was remarkably lower than in the control group for approximately 1 month. CONCLUSION: In this study, the prevalence of GERD in diabetic patient was higher than that found in the general population which suggests that GERD in diabetic patient was due to a poorly controlled serum glucose level and diabetic neuropathy. The chief complaints pertaining to gastrointestinal symptoms in both study groups were non-specific. However, the recovery from symptoms in the GERD group was lower than the control group following drug therapy. The causes of the lower response rate in the GERD group will need to be examined in further studies.
- The Role of cAMP/PKA Activation on Exendin-4-Induced Cyclin D1 Expression in INS-1 Cell.
- Gyeong Ryul Ryu, Jung Hoon Kang, Hwa In Jang, Seung Hyun Ko, In Kyung Jeong, Duck Joo Rhie, Shin Hee Yoon, Sang June Hahn, Yang Hyeok Jo, Myung Suk Kim, Myung Jun Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2005;29(4):295-303. Published online July 1, 2005
- 1,236 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Glucagon-like peptide-1(GLP-1) and exendin-4(EX-4) have been known to induce pancreatic islet proliferation and increases in the betacell mass. Cyclin D1 is a key protein responsible for the entry of the G into the S phase, thereby contributing to cell proliferation. Therefore, the effect of EX-4 on the expression of cyclin D1 in INS-1 cells, a rat pancreatic betacell line, was investigated. The involvement of either mitogen-activated protein kinases(MAPKs) or cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate/protein kinase A(cAMP/ PKA) in the EX-4-induced cyclin D1 expression was also examined. METHODS: INS-1 cells were treated with EX-4 (10 nM), and the cyclin D1 protein levels then determined by Western blot. To investigate the involvement of MAPKs in the EX-4- induced cyclin D1 expression, either a combined treatment of MAPKs inhibitors or transient transfection of extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1 (ERK1) was performed. The effect of cAMP on the EX-4-induced cyclin D1 expression was also examined by treatments with forskolin, an adenylyl cyclase activator, and H-89, a PKA inhibitor. RESULTS: EX-4 increased the expression of cyclin D1 protein in a dose-dependent manner. Although EX-4 induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2, the treatment with PD 98059 or the overexpression of ERK1 had no effect on the EX-4-induced cyclin D1 expression. However, forskolin significantly induced the expression of cyclin D1, whereas the pretreatment of H-89 inhibited the EX-4-induced cyclin D1 expression. CONCLUSION: These results suggest that EX-4 induce cyclin D1 expression in INS-1 cells via cAMP/PKA pathway, but this is not due to ERK activation.
- Mitogenic Effects and Signaling Pathway of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I (IGF-I) in the Rat Beta Cell Line (INS-1).
- In Kyung Jeong, Ja Young Kim, Hyung Joon Yoo, Myung Shik Lee, Moon Kyu Lee, Kwang Won Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2004;28(6):478-489. Published online December 1, 2004
- 984 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Nutrients and growth factors are known to stimulate pancreatic beta cell mitogenesis. IGF-I acts as a survival factor by limiting apoptosis and stimulating proliferation in many cell types. However, the appropriate mitogenic signaling pathways have not been defined. The aim of this study is to elucidate the mitogenic effect and signaling pathways of IGF-I in the rat beta cell line (INS-I). METHODS: The studies were performed using the rat pancreatic beta cell line, INS-1. INS-1 cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 containing serum-free, 0.2% BSA and 11.1 mmol/L glucose media for 24 hours, and the cells were then treated with IGF-I and different concentrations of glucose or tyrosine phosphorylation inhibitors, or insulin. The cell proliferation was measured by the [3H]thymidine uptake and MTT assay. The cell cycle was analyzed by a flow cytometer by using propidium iodide staining. Western blot analyses were performed using antibodies against PY20 and phospho-MAPK. RESULTS: 1) MTT assay and the [3H]thymidine uptake showed that IGF-I stimulated the INS-1 cell proliferation in a dose dependent manner. Glucose was noted to independently increase the INS-1 cell proliferation. A combination of IGF-I and glucose has a synergistic effect on the proliferation of INS-I cells. Insulin did not influence on the mitogenic effect of IGF-I. 2) The S fraction of INS-1 cells treated with IGF-I was increased in a dose dependent manner. IGF-I stimulated the exit from G1 into the S phase of the cell cycle. 3) Investigation of the role of the PI3K and MAPK, by using of the inhibitors LY294002, wortmannin, and PD98059, demonstrated that the activation of MAPK, but not PI3K, required to stimulate the proliferation of INS-1 cells. 4) IGF-I stimulated the phosphorylation activation of pp60 and phospho-MAPK in the INS-1 cells. IGF-I induced the beta cell proliferation, and this was mediated via a signaling mechanism that was facilitated by MAPK. CONCLUSION: The proliferative effect of IGF-I on pancreatic beta cell seems to be mediated through MAPK signaling pathway.
- The Influence of Metabolic Syndrome on the Intima-Medial Thickness and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Type 2 Diabetes.
- Kwang Pyo Son, Young Je Chae, Tae Yu Lee, In Kyung Jeong, Mina Hur, Gu Young Jo, Young Lee, Seong Jin Lee, Chul Young Park, Ki Won Oh, Eon Kyung Hong, Hyun Kyu Kim, Jae Myoung Yu, Doo Man Kim, Sung Hee Lim, Moon Ki Choi, Hyung Jun Yoo, Sung Woo Park
- Korean Diabetes J. 2004;28(5):392-406. Published online October 1, 2004
- 1,279 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Metabolic syndrome (MS) is usually present in type 2 DM (T2DM), and it is associated with atherosclerosis. The aim of this study is to exam the influence of MS on the intima-medial thickness(IMT) and the cardiovascular risk factors for type 2 diabetic patients. SUBJECTS AND METHODS: A cross sectional study was performed on 82 patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) and 84 healthy controls. MS was defined according to the NCEP-ATP III criteria. Those subjects with any history of cerebro vascular accident, ischemic heart disease or acute inflammation were excluded. The cardiovascular risk factors (hsCRP, lipid profile, homocysteine, and uric acid), the status of glucose metabolism (HbA1c, fasting glucose, insulin, and HOMA-IR), the diabetic microvascular complications and the IMT at both common carotid arteries were measured. RESULTS: 1) For patients with T2DM, the levels of waist circumference, blood pressure, TG (1.7+/-1.4 vs 2.2+/-1.4 mmol/L), HDL-C (1.5+/-0.4 vs. 1.3+/-0.3 mmol/L), LDL-C (2.7+/-0.7 vs 3.1+/-0.9 mmol/L), TC/HDL-C (3.5 vs. 41), log of (hsCRP) (-0.11+/-0.4 vs 0.17+/-0.4), mean carotid IMT (0.63+/-0.12 vs. 0.74+/-0.12 mm) and max IMT (0.68+/-0.14 vs. 0.86+/-0.15 mm) were significantly different from the healthy control group. 2) The prevalence of MS in the T2DM groups was 64%. However, a decrease of the waist circumference, as measured by the modified Asian criteria, increased the crude prevalence of MS by up to 75%. 3) Diabetic patients with MS had a higher incidence of hypertension, a lower level of HDL-C, and higher levels of waist circumference, HOMA-IR, TG, and TC/HDL-C, a greater extent of microvasculopathy, an increased log (hsCRP), homocysteine, and carotid IMT than did diabetic patients without MS. 4) Among the component of MS, the presence of hypertriglyceridemia had an influence on the IMT mean and max. 5) The carotid IMT of patients with DM correlated with age, homocysteine, log (hsCRP), and uric acid on univariate analysis, and age and homocysteine we found to be independent risk factors of carotid IMT on multivariated analysis. CONCLUSION: Metabolic syndrome in subjects with glucose intolerance increases the risk of atherosclerosis.
- Activin A Converts Pancreatic Ductal Cells into Insulin-Secreting Cells.
- Kyoung Hee Lee, Mi Kyung Park, Han Wook Kang, Hyun Jin Kim, In Kyung Jeong, Hyung Joon Yoo, Jae Hoon Jeong, Yong Ki Min, Myung Shik Lee, Kwang Won Kim, Moon Kyu Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2004;28(1):20-27. Published online February 1, 2004
- 1,505 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Islet transplantation as a potential treatment for diabetes has been investigated extensively over the past years. One of the major limitations to successful islet transplantation is shortage of insulin-producing tissue, which has stimulated the search for alternative sources, and recently, attention has been focused on the possible use of controlled differentiation of stem cells to obtain specialized cells useful in treating many diseases. It is currently believed that pancreatic progenitor or stem cells exist in the ductal cell population. Activin A is a member of the TGFbeta superfamily, which can block the exocrine pancreatic development and potentiate the endocrine development of the pancreas. In this study, whether activin A could expand and/or differentiate the ductal cells into insulin-producing cells was examined. METHODS: From a collagenase P digested pancreas, ductal tissue was cultured under conditions that allowed expansion as a monolayer, where the cells were overlaid with a rat tail collagen I-coated dish. Activin A cDNA was transfected into rat ductal cells by using Lipofectamine, and the insulin secretion, content and differentiation markers examined. RESULT: The clumps of ductal tissue adhered to the dish 24 hr later, and formed a complete monolayer after 3 days of culture. Activin A overexpression significantly increased both the insulin secretion and content from the ductal cells. The glucose(16.7mM)-induced insulin secretion was also significantly increased. Immunohistochemistry and RT-PCR analyses revealed expression of PDX-1, as well as insulin & GLUT2. CONCLUSION: Activin A overexpression could potentiate the differentiation of pancreatic ductal cells, which might provide a potential new source of cinsulin- producing cells for transplantation
- Effect of Glucose Concentrations on the Cell Proliferation and Expression of L-type Calcium Channel mRNA in Cultured Rat Aortic Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells.
- Young Jung Cho, Hyung Joon Yoo, Hong Woo Nam, Ji Young Suh, In Kyung Jeong, Sung Hee Ihm, Hyeon Kyu Kim, Cheol Young Park, Jae Myung Yoo, Doo Man Kim, Moon Gi Choi, Sung Woo Park
- Korean Diabetes J. 2003;27(3):253-259. Published online June 1, 2003
- 1,174 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) proliferation is one of the major pathogenic mechanisms for atherosclerosis. It is known that L-type calcium channels play a role in VSMC proliferation in diabetic rats. However, there have been no studies that show an association between the L-type calcium channels and the VSMC proliferation due to various glucose concentrations in the culture media. Therefore, the association between the voltage-dependent L-type calcium channels of the VSMCs, and the growth of vascular smooth muscle cells, was examined. METHODS: Rat aortic VSMCs were isolated from the aorta of Sprague-Dawley and OLETF rats, using an enzymic method. The VSMCs were cultured in various concentrations of glucose (5.5, 11.0, 16.6, 25, 30 and 40 mM). The VSMCs (1x10(4) cells in 24-well plates) were incubated in the presence of Bay K 8644 (10(-6)M), both with and without verapamil (10(-6)M), for 48 hours. The proliferation was then assessed by the MTT (methylthiazole tetrazolium) assay, and the expression of L-type calcium channel mRNA by RT-PCR. RESULTS: The vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation was significantly increased, in a dose-dependent manner, with glucose concentrations below 25 mM in both in a dose-dependent manner, with glucose concentrations below 25 mM in both kinds of rat. However, the increase in the VSMC proliferation of the OLETF rat was significantly higher than in the Sprague-Dawley rat. After the Bay K 8644 treatment, with the same glucose concentration, the VSMC proliferation and the expression of L-type calcium channel mRNA were significantly increased in both kinds of rat. After treatment with verapamil, the increased VSMC proliferation and expression of L-type calcium channel mRNA, due to the Bay K 8644, were suppressed to control levels in both kinds of rat. CONCLUSION: The results suggest that below certain concentrations of glucose, 25 mM, the L-type calcium channels may play a role in the VSMC proliferation of OLETF and Sprague-Dawley rats. The growth of the VSMCs in OLETF rats, due to various glucose concentrations (< 25 mM), was significantly higher than in the Sprague-Dawley rats.
- Effects of Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor-gamma(PPARgamma) on the Pancreatic beta Cell Proliferation.
- Jung Hyun Noh, Tae Young Yang, In Kyung Jeong, Jae Hun Chung, Yong Ki Min, Myung Shik Lee, Kwang Won Kim, Moon Kyu Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2003;27(3):241-252. Published online June 1, 2003
- 1,115 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The effects and mechanisms of PPARgamma ligands on the cell proliferation in pancreatic beta cells were examined. METHODS: PPARgamma 1 cDNA was overexpressed in INS-1 cells using an adenoviral vector. The cell proliferations were measured by the MTT assay method, following the treatments with troglitazone (TGZ), rosiglitazone (RGZ), 15d-prostaglandin J2 (15d-PGJ2) or retinoic acid (RA), at increasing doses, in INS-1 and PPARgamma overexpressed INS-1 cells. The apoptosis, telomere length and cell cycles were determined after the PPARgamma ligand treatment. RESULTS: The long-term incubation, with PPARgamma ligands over 24 hr, inhibited the INS-1 cell proliferation rate. Apoptosis was not observed with the PPARgamma ligand treatment. G1 cell cycle arrest was observed with the troglitazone treatment. The telomere length remained unchanged following the TGZ treatment. The basal cell proliferation rate was unaffected by the overexpression of PPARgamma . After 48 h of TGZ treatment, the proliferation of the INS-1 cells was inhibited, in a dose- dependent manner, both with and without the overexpression. Moreover, the degree of inhibition was exaggerated in the PPARgamma overexpressed cells compared to beta gal overexpressed cells. CONCLUSION: PPARgamma ligands have direct inhibitory effects on the proliferation of INS-1 cells. Although the basal cell proliferation rate was not affected by PPARgamma overexpression, the PPARgamma overexpression and PPARgamma ligands have a synergistic inhibitory effect on the cell proliferation rate in pancreatic beta cells. G1 cell cycle arrest may be involved in the reduction of cell proliferation due to PPARgamma ligands.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





